Cloud Computing has revolutionized how businesses access, manage, and scale their IT resources. Among the various cloud service models, Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) stand out as the most widely used. Each of these models offers distinct services tailored to meet diverse business needs and technical capabilities.
In this article, we’ll find out the difference between IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS and understand which one of these cloud computing service models fits your needs the most.
What Cloud Computing is
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence via the internet, commonly known as “the cloud.” This approach facilitates quicker innovation, adaptable resources, and cost efficiencies.
By paying solely for the cloud services you utilize, you can effectively reduce your operating expenses, enhance the efficiency of your infrastructure, and adapt your resources in line with your evolving business requirements.
Generally speaking, cloud computing is available in a variety of service models based on your desired level of control and accountability. IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS are the three main models.
What Is IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)?
Infrastructure as a Service, commonly referred to as IaaS, represents a cloud computing model that allows you to rent IT infrastructure—such as servers, storage, and networking via the internet, rather than purchasing and managing it on your own.
In the past, when a company aimed to operate an application, it needed to acquire physical servers, set them up, and manage all aspects from power supply to temperature control. A cloud provider takes care of all that with IaaS. Just log in, select the resources you require, and begin your building process.
The top IaaS providers are known for delivering dependable cloud infrastructure services, fostering a strong sense of trust with their clients. Leading providers offer a wealth of resources designed to meet every business requirement, ensuring your company can grow smoothly and efficiently. DigitalOcean, Amazon Web Services, Google Compute Engine and Linode are a few of the most widely recognized and reliable IaaS providers.
When to use IaaS?
IaaS can be used to enhance the operations of any business, regardless of size. Owners of startups or small businesses may value the time and money that IaaS can save them by eliminating the need to manufacture or purchase new hardware and software. IaaS is frequently used by larger businesses to keep control over their infrastructure without having to buy software or programs they won't use. IaaS's flexibility allows it to run on different hardware or software based on a company's requirements, which is advantageous for rapidly expanding businesses.
Pros:
- More control
- Flexibility
- Increased performance
Cons:
- Needs manual setup and maintenance
- Security risks
- Unexpected cost
Best for: Teams seeking control, flexibility, and scalability, while avoiding physical infrastructure ownership.
What Is PaaS (Platform as a Service)?
Platform as a service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model type that equips developers with a robust platform to construct, deploy, and oversee applications, all while decreasing concerns about the underlying infrastructure. This enables developers to concentrate on coding, as the cloud provider takes care of the infrastructure, maintenance, and scalability aspects.
PaaS encompasses all the essential components required for application development, such as operating systems, runtime environments, databases, development tools, middleware, along with hosting and scaling functionalities.
Heroku, Microsoft Azure, and Google App Engine are among the most famous examples of PaaS providers.
When to use PaaS?
If you’re a developer working alongside others on a shared project, PaaS could be the perfect fit for your needs. This platform empowers developers to expedite their workflow and craft tailored applications, ultimately saving both time and resources for developers and companies during the development or launch phases of new applications. PaaS encompasses services that assist developers throughout the development process, utilizing web services and databases for information storage. This makes it an excellent choice for users engaged in creating new applications or managing substantial amounts of data.
Pros:
- Faster time to market
- Affordable access to sophisticated tools
- Scalable
- Predictable cost
Cons:
- Vendor dependence
- Security vulnerability
- Limitations in terms of customization and control
Best for: Developers and companies who want to rapidly design, launch, and grow apps without maintaining infrastructure .
What Is SaaS (Software as a Service)?
Software as a Service functions through a cloud-based framework, with applications hosted by a service provider and accessible via the internet. Rather than buying and setting up software on individual computers or servers, users select a subscription model, accessing the software online. For companies aiming to create scalable and efficient cloud applications, investing in SaaS development services can effectively utilize this architecture to provide high-performing, cost-effective solutions.
Upon subscribing to a SaaS application, customers usually access it via a web browser. The application operates on the servers of the service provider, which manage all processing and data storage tasks. This enables users to utilize the software from any device connected to the internet, ensuring both flexibility and mobility.
When to use SaaS?
Choosing SaaS could be a wise decision if you're a small business owner or member of a startup and want to offer your clients an e-commerce solution. SaaS enables quick setup and user distribution by doing away with the requirement for dedicated servers to access applications. For short-term projects or software that you may use occasionally, like tax software, SaaS can be a great option. Additionally, you can use SaaS to create and distribute any applications that require internet and mobile connectivity.
Pros:
- Easy to install and use
- No technical knowledge or team required
- Accessible over the Internet from any device
Cons:
- Almost no customization
- Service disruptions
- Unavailable without an Internet connection
Best for: SMEs and individuals who need ready-to-use software without installation, maintenance, or infrastructure administration.
Side-by-Side Comparison: IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS
To make the difference between IaaS PaaS, and SaaS clearer, here’s a quick side-by-side breakdown that highlights how each model compares in terms of usage, flexibility, cost, and more.
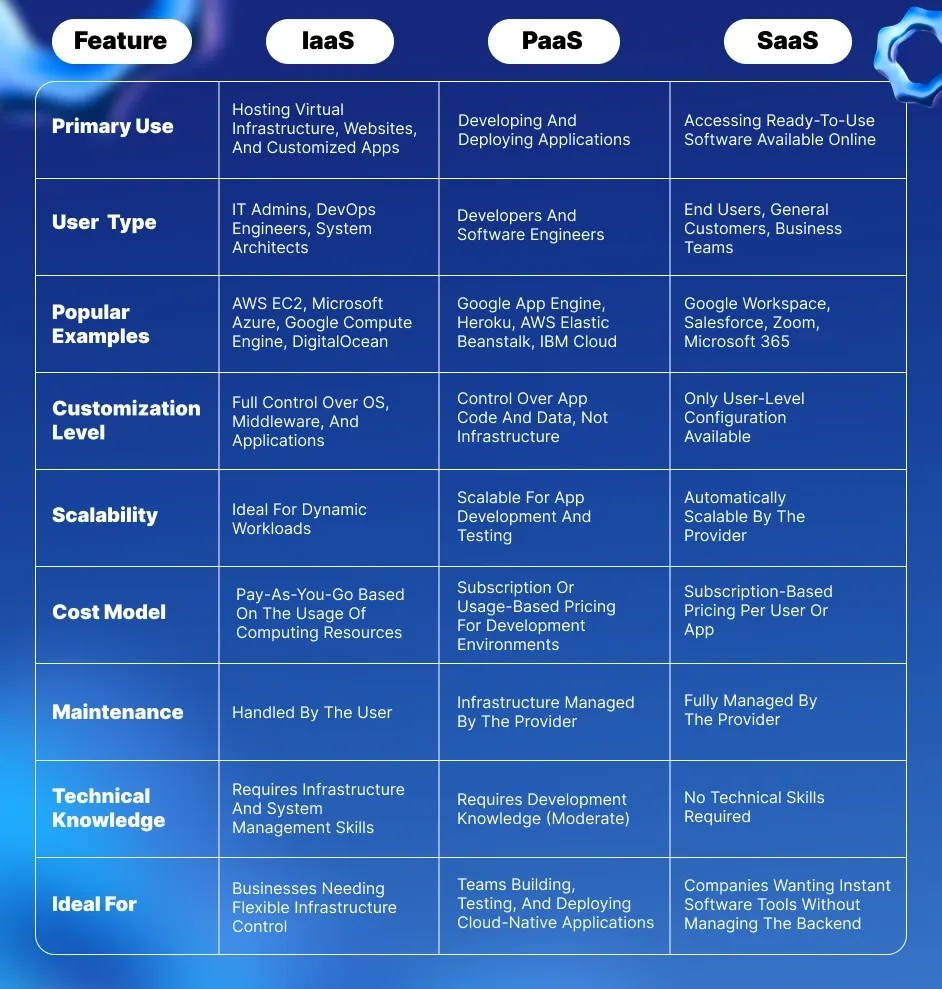
PaaS vs SaaS
The main distinctions between PaaS and SaaS may have an impact on who and how they are used. PaaS and SaaS differ in the following areas:
- Control: With PaaS, developers are in charge of creating and organizing their own apps and data. On the other hand, because SaaS services are managed by third-party providers via cloud computing, users do not have control over the apps or data.
- User base: Web developers and anyone else involved in the creation of computer programs or applications are big fans of PaaS. SaaS may be preferred by small enterprises and individual users who want to make their apps available to clients.
- Access: Although PaaS provides a platform for developers to create new programs and applications, those programs and applications need access to the original server or operating system on which the developers built them. SaaS apps can be accessed from any location with an internet connection, and occasionally they offer mobile platforms as an option.
- Goal: PaaS enables users to concentrate on creating new applications by potentially cutting down on the amount of time spent managing various infrastructure types. Users seeking quick organization or data management solutions, like launching apps or storing data, like emails, are the main beneficiaries of SaaS applications.
- Foundation: A lot of developers use pre-existing IaaS platforms to create PaaS applications. Similar to this, developers frequently build SaaS applications by building upon IaaS or PaaS applications.
IaaS vs PaaS
- Control: With IaaS, users have control over virtual machines, storage, and networking components. They can configure the operating system and install custom software. For PaaS, developers focus on creating and organizing their apps, but the underlying infrastructure is managed by the provider, limiting control over hardware and the operating system.
- User Base: IaaS is favored by system administrators, DevOps teams, and IT professionals who need full control over their infrastructure. PaaS, on the other hand, is primarily used by application developers looking to streamline the development process without managing infrastructure.
- Access: IaaS provides access to raw infrastructure components like virtual machines, which users configure as needed. PaaS provides a platform that includes development tools, middleware, and runtime environments, abstracting much of the infrastructure, so developers can focus on building applications.
- Goal: IaaS aims to offer scalable, flexible infrastructure for custom IT setups, giving users complete control over the virtualized resources. PaaS focuses on simplifying the app development and deployment process, reducing the need for managing infrastructure, and enabling faster time-to-market.
- Foundation: IaaS forms the foundation for PaaS, as PaaS platforms are built on top of the infrastructure provided by IaaS. Similarly, PaaS enables developers to build applications more efficiently by abstracting away the complexities of infrastructure management.
XaaS: Everything as a service
Everything as a Service, or XaaS, is a general term used to describe the increasing variety of services offered online. It includes all cloud-based services, such as the three main service models in cloud computing: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
Fundamentally, XaaS is about providing users with on-demand access to all forms of IT resources, including platforms, software, storage, security, infrastructure, and even business processes. Businesses can scale swiftly, cut capital costs, and concentrate on innovation rather than infrastructure management thanks to this adaptable model.
The shift from "as-a-service" models to XaaS illustrates how widespread cloud computing has become in contemporary corporate operations. All three models, IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, offer distinct advantages, but when combined, they serve as the cornerstone of an IT ecosystem that is scalable and service-based.
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: Statistics
Here are some statistics that highlight the current state and adoption trends of cloud computing models, specifically, IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
With a projected growth rate of more than 22% for 2025, the cloud computing market as a whole is expected to expand over the coming years. In addition, it is anticipated that the global market for public cloud services will surpass 723 billion dollars by 2025.
In 2023, IaaS accounted for more than 25% of the total cloud computing market. Revenues from public cloud IaaS are anticipated to increase dramatically over the next several years, from approximately 115 billion USD in 2022 to over 211 billion USD by 2025. Nonetheless, it is anticipated that the market share of cloud infrastructure will decline in favor of the PaaS market's encouraging growth. However, with over 299 billion dollars in revenue annually, SaaS remains and will remain the largest segment of the entire cloud computing market.
The public cloud PaaS market generated over 171 billion dollars in revenue in 2024 according to recent statistics. In 2025, the PaaS market is anticipated to expand by more than 21% due to the growing popularity of AI-powered platforms.
The leading companies in the global PaaS market are Google Cloud Platform, IBM Cloud, Amazon Web Services, and Microsoft Azure. Over 47% of the global IaaS and PaaS market is held by Microsoft and Amazon combined. According to recent surveys, a large number of users are either testing, already using, or intend to use platforms offered by these service providers. The PaaS market is expected to continue growing and innovating as more companies adopt cloud solutions.
Statista claims that in 2024, the global SaaS market brought in about $250 billion, or roughly two-thirds of the total revenue from the public cloud services market. SaaS revenue growth is not anticipated to slow down in the upcoming years, but its market share of cloud services will likely decrease as cloud platform and infrastructure services grow.
How to Choose the Right Model for Your Business?
Understanding the difference between IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS is crucial to aligning your IT strategy with your business goals. Your company goals, technical capacity, and desired level of control over your IT resources will determine which of IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS you choose. Every model in the spectrum of cloud computing service models has special advantages; knowing their variations will enable you to make a better, more reasonably priced choice.
When weighing IaaS against PaaS against SaaS, take these important considerations:
- IaaS could be the best option if your team requires complete control over operating systems, servers, and storage. In cloud computing, wondering what IaaS is? Perfect for system managers and DevOps teams, this is the model that provides you raw infrastructure resources delivered over the clouds.
- PaaS simplifies development with built-in tools, runtime environments, and scalability if your main concentration is on creating and running apps without backend management. For development teams seeking speed free from infrastructure setup concerns, it's perfect.
- SaaS is the best fit for companies seeking ready-to-use solutions with minimum setup. From CRM systems to email tools, SaaS calls for just log-in and go—no maintenance or updates from your end.
How does Solicy help?
At Solicy, we specialize in custom software development with deep expertise across all major cloud computing service models. We offer end-to-end IaaS, PaaS and SaaS development services, from idea validation and design to deployment and scaling.
Whether you're building cloud infrastructure, developing a robust application platform, or launching a full-scale product, we provide the technical foundation and strategic guidance to ensure success. With a focus on quality, performance, and scalability, Solicy transforms your vision into a reliable, future-ready solution.
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: FAQs
Which Common Cloud Service Model Offers the Customer the Most Control of the Cloud Environment?
Out of the three main models of cloud computing services, IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) gives the consumer the most control. Users of IaaS handle the operating system, storage, implemented apps, and occasionally even portions of the networking configuration.
Which Option Refers to a Combination of the Three Main Services in Cloud Computing?
XaaS stands for all kinds of cloud-based services and reflects the rising trend of providing storage, security, databases, and even corporate processes as a service in addition to infrastructure, platforms, and software.







